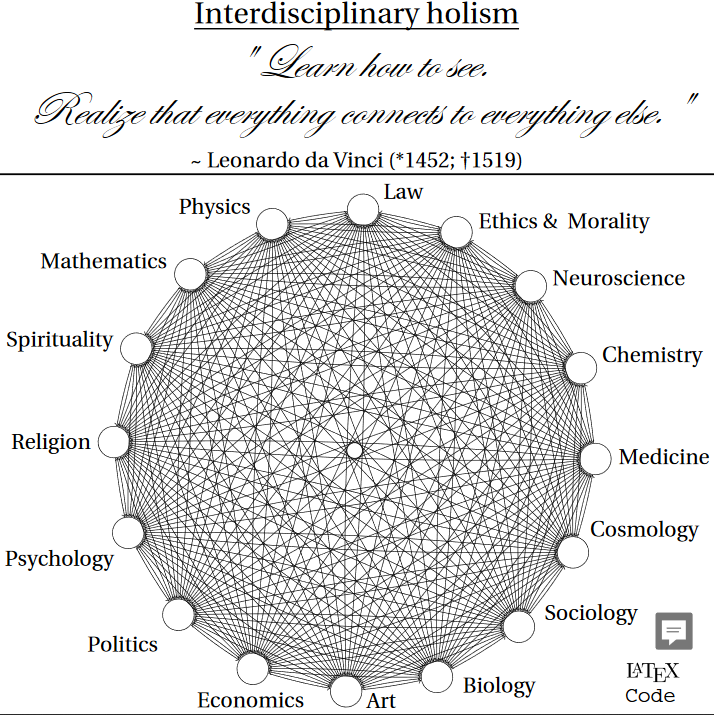
LaTeX (/ˈlɑːtɛx/ LAH-tekh or /ˈleɪtɛx/ LAY-tekh;[1] a shortening of Lamport TeX) is a document preparation system.[2] When writing, the writer uses plain text as opposed to the formatted text found in WYSIWYG (“what you see is what you get”) word processors like Microsoft Word, LibreOffice Writer and Apple Pages. The writer uses markup tagging conventions to define the general structure of a document (such as article, book, and letter), to stylise text throughout a document (such as bold and italics), and to add citations and cross-references. A TeX distribution such as TeX Live or MikTeX is used to produce an output file (such as PDF or DVI) suitable for printing or digital distribution. Within the typesetting system, its name is stylised as LaTeX.


![grepWin: Regular expression search within large text corpora e834b50e2df6043ecd0b4401ef444f94eb6ae3d01db3144297f4c871_640[1]](https://cognitive-liberty.online/wp-content/uploads/e834b50e2df6043ecd0b4401ef444f94eb6ae3d01db3144297f4c871_6401-300x300.png)

![Nescience vs. ignorance (on semantics and moral accountability) eb32b70e21f51c3e815b410cee45449efe76e7d01bb6124490f7c2_640[1]](https://cognitive-liberty.online/wp-content/uploads/eb32b70e21f51c3e815b410cee45449efe76e7d01bb6124490f7c2_6401-300x200.jpg)
![Aldous Huxley - The Ultimate Revolution (Berkeley Speech 1962) Huxley[1]](https://cognitive-liberty.online/wp-content/uploads/Huxley1-300x300.jpg)
![Parapsychology: CIA testing Uri Geller e835b00c2df6013ecd0b4401ef444f94eb6ae3d01db3164094f0c971_640[1]](https://cognitive-liberty.online/wp-content/uploads/e835b00c2df6013ecd0b4401ef444f94eb6ae3d01db3164094f0c971_6401-300x220.jpg)